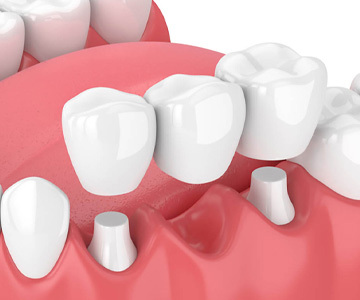
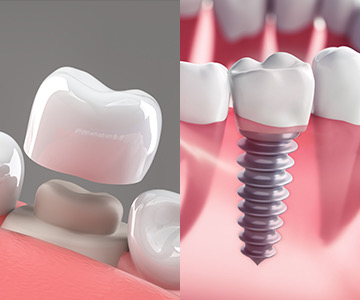
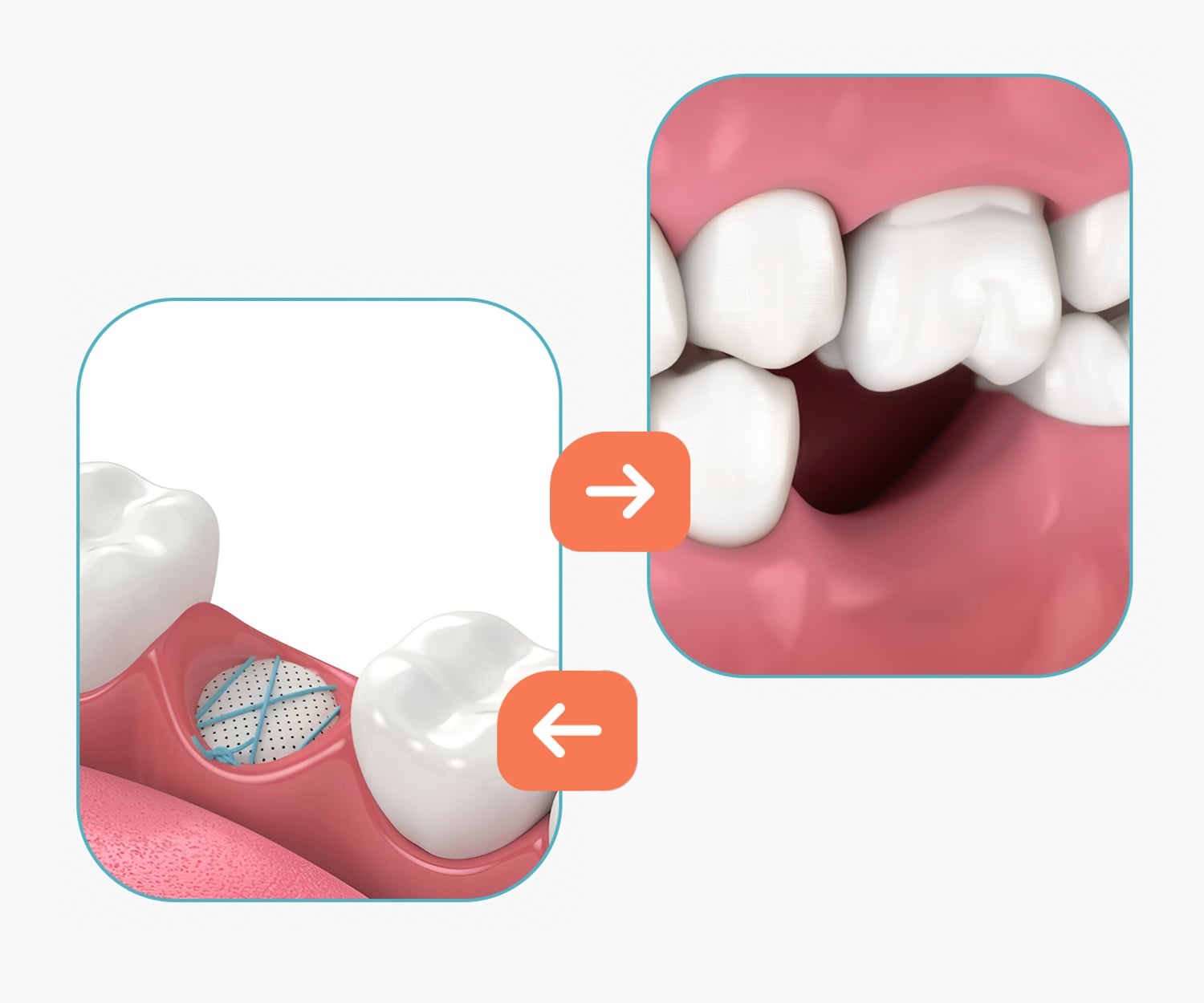
Treatment of edentulism (missing teeth) with a dental bridge is one of the most common and effective methods. A dental bridge allows for the restoration of both chewing function and smile aesthetics. It is a fixed prosthetic construction that is supported by healthy adjacent teeth and fills the space of a missing tooth. In this article, we will discuss what a dental bridge is, the types available, and how the placement process is carried out.
To book a visit, sign up for a consultation. To clarify the details, our operator will contact you.

Impact of tobacco on oral health
20 April 2022
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 1.3 billion people today consume tobacco. Tobacco poses a serious threat to us, regardless of the form in which we consume it. It is most commonly found in the form of cigarettes and contains the alkaloid (physiologically active, basic, nitrogen-containing organic compounds.) Nicotine, which is addictive. Smoking negatively affects almost every organ in our body and increases the risk of various diseases. It also significantly aggravates the health conditions that patients have experienced before, albeit with much milder symptoms.
What effect does tobacco have on oral tissues?
For a charming smile, clean and white teeth, just taking care of them at home, flossing and using antibacterial fluids is not enough. By smoking, swallowing and inhaling tobacco smoke the gums become irritated and the teeth turn yellow, and in many cases stomatitis also develops. The most common cause of stomatitis is mechanical damage to the mucous membrane (depending on external factors) and it mostly spreads in the form of painful erosions and ulcers. Tobacco also has a negative effect on the gums. Studies have shown that nicotine narrows the blood vessels that nourish the gums and tooth tissues, ie the microcirculation (blood circulation) in the mouth is disrupted, the gum tissue thickens and the risk of premature tooth decay or loss is increased.
What is the connection between tobacco and oral cancer?
It is known that tobacco consumption is a major risk factor for oral cancer and many other cancers. Oral cancer develops when DNA mutations occur in cells of the lips or oral tissues. As a result of mutation, cancer cells multiply uncontrollably and this process becomes irreversible. An accumulation of cancer cells in the oral cavity (a single mass of tumor cells) forms a tumor. Over time, cancer cells may spread to other parts of the head and neck or to other parts of the body. Any tobacco product, including cigarettes, cigars, and chewing tobacco, contains nicotine, carcinogens (chemicals, physical radiation, or oncogenic viruses whose effects on humans or animals increase the likelihood of developing malignant tumors) and various toxins. Cigarettes are the most common form of tobacco, which poses a particularly serious threat to human oral health. According to The American Lung Association. Smokers are 10 times more likely to develop oral cancer than non-smokers.
When should we consult a doctor?
"Blits Dental - Kakhaber Kharebava dental clinic" recommends that you pay special attention to the health of your oral cavity and consult a doctor immediately if you experience any of the symptoms listed below. Symptoms of oral cancer:
- Pain that does not go away
- A bulge or thickening of the skin in the lining of the mouth
- White or reddish spot on the inside of the mouth
- Decayed teeth
- Restriction of prosthesis making
- Tongue pain
- Lower jaw pain and burning
- Painful or difficult chewing
- Painful or difficult swallowing
- Sore throat
- The feeling that something is in the throat
Early diagnosis is crucial. For this purpose it is necessary to periodically inspect all areas of the oral cavity and perform a biopsy in case of tissue changes
How do I stop smoking ?
"Blits Dental - Kakhaber Kharebava dental clinic" presents tips developed by the American Cancer Society ACS to help you quit smoking and regain a white, healthy and charming smile:
- Think often about the reasons why you want to quit.
- Choose a stress-free time to quit smoking.
- Start doing exercises or activities every day to reduce stress and improve your health.
- Relax a lot and eat balanced, vitamin-rich foods.
- Participate in a smoking cessation program or other support group.
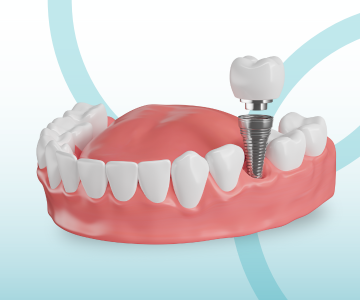
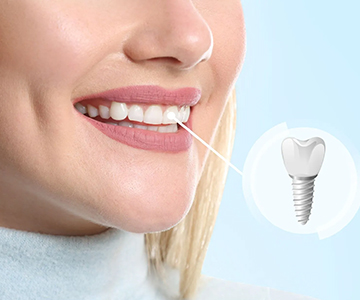
Missing teeth are no longer a problem! Dental implants offer the most advanced, durable, and natural-looking solution for restoring your smile. An implant, together with its crown, mimics a real tooth both aesthetically and functionally-helping you regain confidence, comfort, and a complete smile.
During pregnancy, hormonal changes can cause gum inflammation, bleeding, enamel erosion, and an increased risk of cavities. That’s why visiting the dentist during pregnancy is especially important.
Gnathology is one of the leading branches of 21st-century dentistry. It forms the foundation for any complex dental treatment planning
Tooth loss (edentulism) affects not only the appearance of your smile but also the overall functional health of your oral cavity
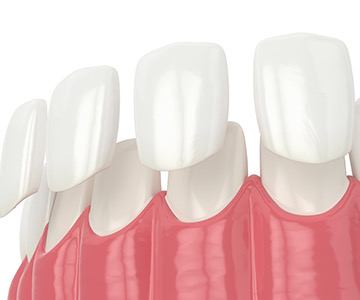
Dental veneers can be made from various materials, but ceramic (porcelain) veneers are the most widely used.
Modern aesthetic and functional dentistry is continually evolving, striving to identify restorative materials that combine exceptional strength
The eruption of baby teeth is one of the most important stages in a child’s early development.
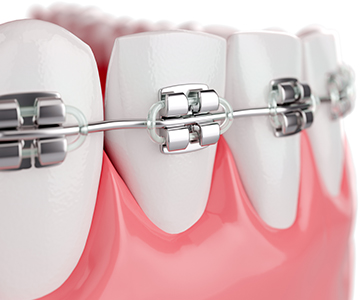
Modern dentistry increasingly emphasizes the importance of orthodontic care.
Oral health care begins long before the first permanent tooth erupts.
A smile is one of the key elements of a person’s visual identity. It conveys confidence and positivity. However, the beauty of a smile is not only an aesthetic factor—it is directly connected to oral health.
Orthodontic treatment has long gone beyond the limits of traditional metal braces.
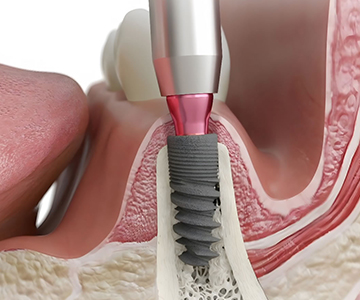
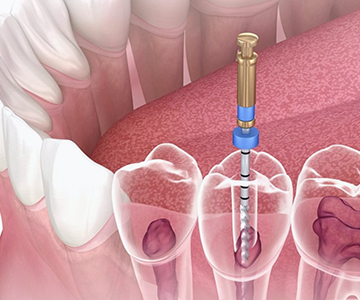
Dental implantation is the best method for restoring missing teeth. However, for the procedure to be successful, the jawbone must have sufficient volume and density.
Dental implantation is one of the most effective and safest surgical procedures in modern dentistry for restoring missing teeth.
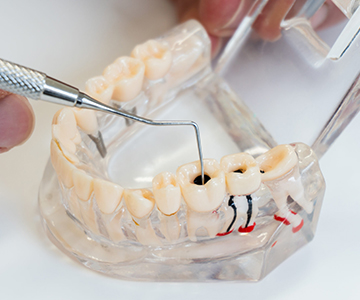
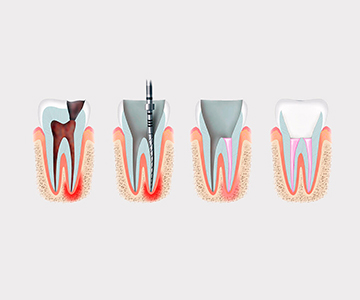
Initial endodontic (root canal) treatment is usually successful and helps preserve the natural tooth.
Root canal treatment, also known as endodontic therapy, is one of the most frequently discussed yet often misunderstood dental procedures.
Tooth decay is one of the most common dental conditions, involving damage to the hard tissues of the teeth
Modern dentistry is constantly evolving, offering improved methods for solving complex issues.
Today, there are numerous teeth whitening options—both at home and professionally done.






.jpeg)
.jpeg)