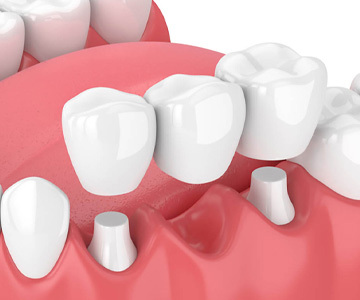
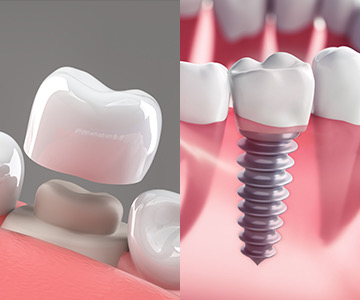
Treatment of edentulism (missing teeth) with a dental bridge is one of the most common and effective methods. A dental bridge allows for the restoration of both chewing function and smile aesthetics. It is a fixed prosthetic construction that is supported by healthy adjacent teeth and fills the space of a missing tooth. In this article, we will discuss what a dental bridge is, the types available, and how the placement process is carried out.
To book a visit, sign up for a consultation. To clarify the details, our operator will contact you.
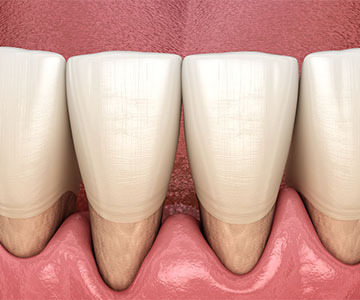
What causes gingival recession?
19 April 2023
A healthy gum shape and color is an integral part of a charming smile. There are many cases when the gum around the teeth is uneven in shape or height, and because of this, the teeth appear to be different sizes. Nowadays, there are many clinical cases where the main problem is the recession of the gingival tissues. The process of gum recession involves the gradual upward movement of the gum and exposure of the root. Gradually, the gum tissue no longer covers the root of the tooth, which visually makes the tooth appear longer and unaesthetic. Gingival recession is a fairly common disease in both young and middle-aged patients. The problem develops slowly and painlessly. Often, the patient does not even know that there is recession of the gums, because the receding of the gums is a long process and the visual problem shows itself only at the last stage. As for the primary symptoms, the first sign of recession can be increased sensitivity of the tooth, also the patient's own tooth may seem longer than before.
What causes gum recession?
The causes of gum recession are quite diverse and are mostly individual for each patient. Some people are genetically predisposed to having thin gums, which makes them more prone to recession. If you have naturally thin and weak gums, it is especially important to maintain your oral health by scheduling frequent dental visits and using toothpastes and mouthwashes that will strengthen and heal your gums and prevent future complications. In addition to genetic factors, receding gums can be caused by various environmental factors. These can be:
- Periodontal diseases - periodontitis;
- Removable prostheses - the metal brackets of the prostheses may injure the supporting teeth and cause gum recession;
- Natural stretches on the lips - sometimes, genetically, the stretches on the lips are located in such a way in relation to the teeth that when talking and eating, the gum tissue is constantly pulled, which provokes recession;
- tobacco consumption;
- Rough, intense and forceful cleaning of teeth;
- Permanent use of abrasive toothpaste.
- poor oral hygiene and accumulated bacterial plaque (tartar);
- Gum recession is also often found in patients undergoing orthodontic treatment (braces).
When should we consult a doctor?
For the most part, patients with receding gums turn to dentists at the last stage of the disease. In a normal case, the gum completely covers the root of the tooth and only the crowns of the teeth are visible in the mouth, however, during recession, this norm is violated and the root of the tooth can be seen freely. Accordingly, the symptomatic manifestation of recession for the patient is, first of all, aesthetic discomfort. Due to the upward movement of the gum (while lowering the lower jaw), the root of the tooth appears in the mouth, therefore, the tooth appears visually elongated. Increased sensitivity also causes discomfort to the patient. If the root of the tooth is not covered by the gum, there is hypersensitivity, mainly when the patient drinks a cold drink. During gingival recession, patients are at risk of caries, because when gingival recession develops and the root of the tooth is no longer covered by gum, it is easily accessible to bacteria, which in itself implies the risk of root cavities (caries).
Blitz Dental - Kakhaber Kharebava Clinic advises you to contact a professional as soon as you discover problems with your gums. If, after a visual inspection, you feel that your teeth are "longer" and your gums are "shorter", definitely schedule a visit to the dentist.
What is the treatment for gum recession?
Treatment of gum recession depends on the degree of recession - how high the degree of gum recession is. Anatomically, the gum does not grow back, however, it is possible to mobilize the gum tissue and cover the root of the tooth with microsurgical intervention. In order to achieve a harmonious effect with the patient's oral cavity and facial features, the most proven method is the use of mathematical principles, which takes into account the "golden section" of the crowns and gums in patients with disturbed aesthetics, the pre-determination of biological boundaries and the protection of these boundaries during surgical intervention.
Modern aesthetic dentistry offers patients many different methods that can not only maintain healthy gums and oral cavity, but also correct existing defects using an invasive method. Surgical intervention used during gum recession ensures the health of the patient's mouth and returns him to a healthy charming smile.
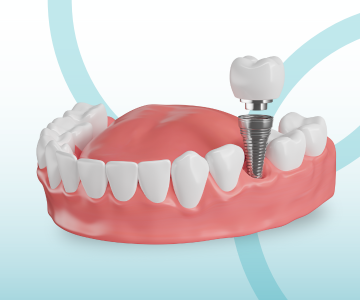
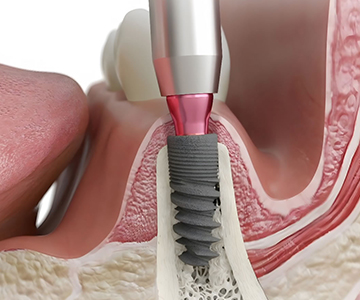
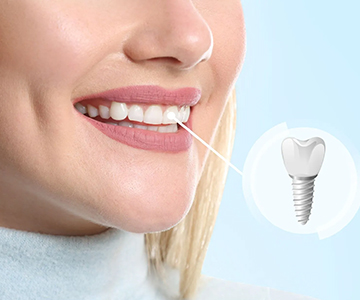
Missing teeth are no longer a problem! Dental implants offer the most advanced, durable, and natural-looking solution for restoring your smile. An implant, together with its crown, mimics a real tooth both aesthetically and functionally-helping you regain confidence, comfort, and a complete smile.
During pregnancy, hormonal changes can cause gum inflammation, bleeding, enamel erosion, and an increased risk of cavities. That’s why visiting the dentist during pregnancy is especially important.
Gnathology is one of the leading branches of 21st-century dentistry. It forms the foundation for any complex dental treatment planning
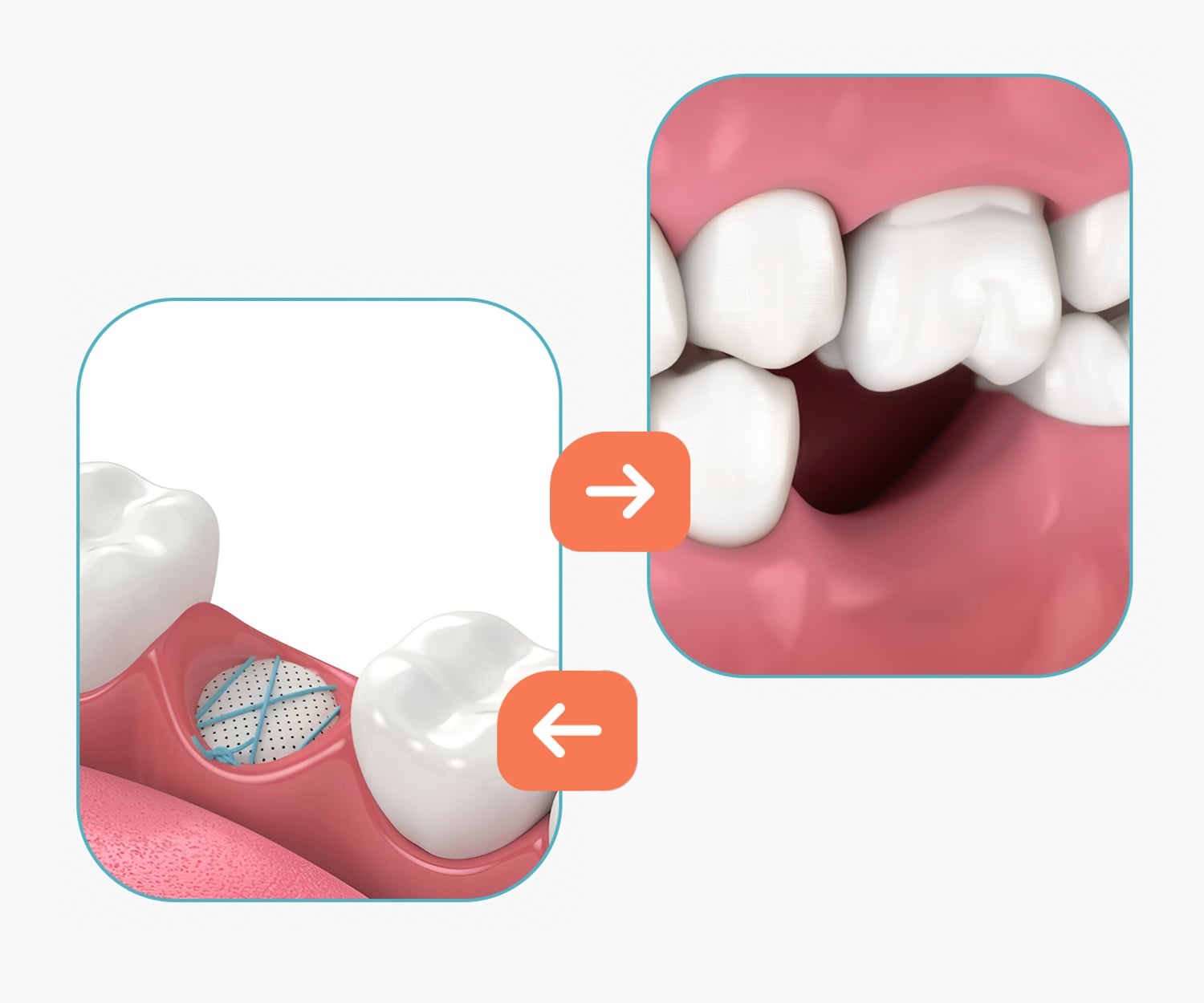
Tooth loss (edentulism) affects not only the appearance of your smile but also the overall functional health of your oral cavity
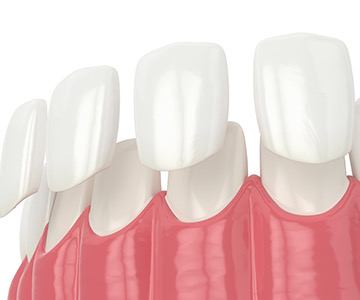
Dental veneers can be made from various materials, but ceramic (porcelain) veneers are the most widely used.
Modern aesthetic and functional dentistry is continually evolving, striving to identify restorative materials that combine exceptional strength
The eruption of baby teeth is one of the most important stages in a child’s early development.
Modern dentistry increasingly emphasizes the importance of orthodontic care.
Oral health care begins long before the first permanent tooth erupts.
A smile is one of the key elements of a person’s visual identity. It conveys confidence and positivity. However, the beauty of a smile is not only an aesthetic factor—it is directly connected to oral health.
Orthodontic treatment has long gone beyond the limits of traditional metal braces.
Dental implantation is the best method for restoring missing teeth. However, for the procedure to be successful, the jawbone must have sufficient volume and density.
Dental implantation is one of the most effective and safest surgical procedures in modern dentistry for restoring missing teeth.
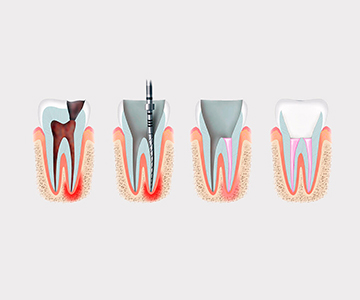
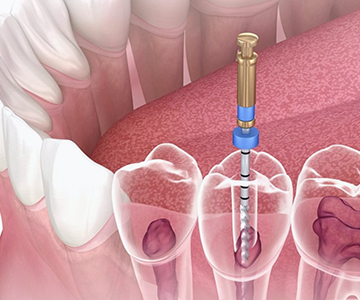
Initial endodontic (root canal) treatment is usually successful and helps preserve the natural tooth.
Root canal treatment, also known as endodontic therapy, is one of the most frequently discussed yet often misunderstood dental procedures.
Tooth decay is one of the most common dental conditions, involving damage to the hard tissues of the teeth
Modern dentistry is constantly evolving, offering improved methods for solving complex issues.
Today, there are numerous teeth whitening options—both at home and professionally done.






.jpeg)
.jpeg)