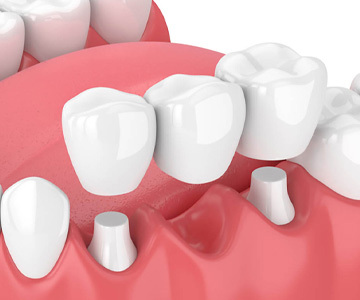
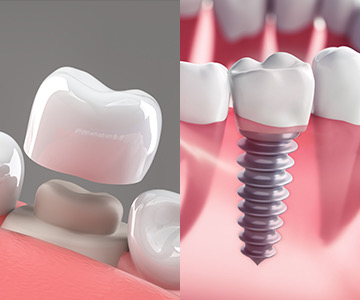
Treatment of edentulism (missing teeth) with a dental bridge is one of the most common and effective methods. A dental bridge allows for the restoration of both chewing function and smile aesthetics. It is a fixed prosthetic construction that is supported by healthy adjacent teeth and fills the space of a missing tooth. In this article, we will discuss what a dental bridge is, the types available, and how the placement process is carried out.
To book a visit, sign up for a consultation. To clarify the details, our operator will contact you.
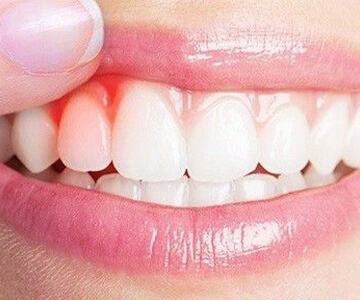
Periodontology and Periodontitis
18 November 2021
Periodontics It is one of the most important fields of dentistry that studies various diseases of the gums and is responsible for the health of your oral cavity. The periodontium is a collection of tissues. Its components are gum, the alveolar bone, the occlusal covering of the tooth's root surface, and the periodontium that connects the concussion to the bone around it. The periodontium combines the soft and hard tissues around the tooth and contributes to both the health of the oral cavity and the strength of the tooth in the jaw bone.
Periodontal status can say more about our general health than just what happens in the oral cavity. Plaque on the teeth can provoke many systemic diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and others.
As for periodontitis - Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the tissues around the tooth that can lead to tooth loss. Periodontal disease is one of the most common diseases in the world, affecting almost 90% of the total population (every 8 out of 10 people over the age of 35 report certain types of gum complaints). There are different types of periodontal disease, but most of them are caused by bacterial plaque accumulated in the oral cavity. The multiplication of such pathogenic bacteria develops inflammation of the gums, followed by tooth decay in the jawbone, bone loss, and eventually tooth loss.
How does periodontitis develop?
As a result of the accumulation of plaque on the tooth surface and around the gums, pathogenic (disease-causing) bacteria multiply rapidly, resulting in the development of gingivitis or inflammation of the gums. If the patient is not given proper anti-inflammatory treatment, the bacteria will penetrate deeper into the deeper layers of the tooth root surface and develop periodontal disease. In addition to a plaque, the cause of periodontitis can be:
- Impaired immunity
- Genetic factor
- Frequent consumption of tobacco
- Side effects of drug treatment
- Stress
- Improper nutrition
As for the symptoms of periodontitis, they are characterized by diversity and are mainly manifested in bleeding gums. In addition, periodontitis is characterized by visual and hygienic discomfort, which means increased red gums and an unpleasant odor in the mouth.
In what cases should we consult a periodontist?
Bleeding from the gums is often ignored by patients, which can lead to severe consequences. The development of inflammatory diseases of the periodontium (gingivitis and periodontitis) begins in the gums. It covers all the tissues around the tooth. During gingivitis, you may notice only a slight reddening of the gums, minor bleeding, and an unpleasant taste. This stage is painless, but remember that this is the first stage in the development of periodontal disease, and only at this stage is the process reversible, so a complete cure is possible. Without proper treatment, gingivitis develops into periodontitis - when the inflammatory process has already spread to the bone. The treatment can stop the aggressive process, however, it requires constant supervision so as not to resume and continue to progress. Without treatment in the late stages of periodontal inflammatory disease, the teeth become so brittle that it is impossible to maintain them. As a result, completely healthy teeth are often lost.
Treatment of periodontitis
In most cases, periodontal treatment is successful. Treatment of periodontitis always starts with conservative (removal of plaque) methods and in cases when conservative treatment is not enough resort to surgical methods of treatment. Conservative treatment begins with the removal of the gums above and below the gums of the teeth. Provocative factors, such as carious cavities, blemishes, and artificial crown defects, must be removed after cleansing. According to the indications, medical treatment is prescribed and the patient is referred for dispensary observation.
Ways to prevent periodontitis
The best way to prevent the inflammatory process of the gums is to maintain general hygiene and constant control. See a dentist once every 6 months for cleaning and scheduled observations. Regular observation will guarantee that your smile will always be charming.
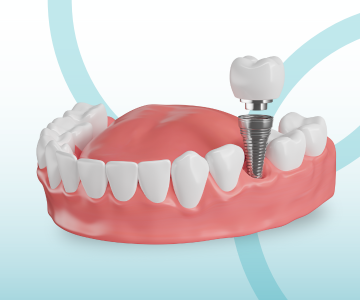
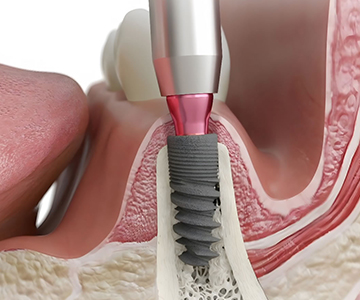
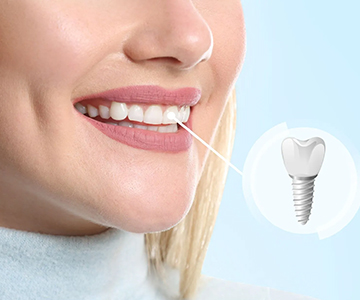
Missing teeth are no longer a problem! Dental implants offer the most advanced, durable, and natural-looking solution for restoring your smile. An implant, together with its crown, mimics a real tooth both aesthetically and functionally-helping you regain confidence, comfort, and a complete smile.
During pregnancy, hormonal changes can cause gum inflammation, bleeding, enamel erosion, and an increased risk of cavities. That’s why visiting the dentist during pregnancy is especially important.
Gnathology is one of the leading branches of 21st-century dentistry. It forms the foundation for any complex dental treatment planning
Tooth loss (edentulism) affects not only the appearance of your smile but also the overall functional health of your oral cavity
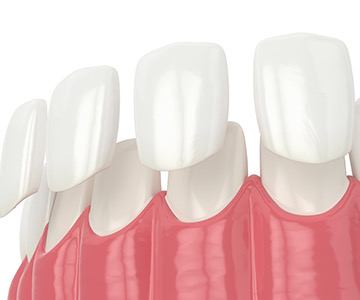
Dental veneers can be made from various materials, but ceramic (porcelain) veneers are the most widely used.
Modern aesthetic and functional dentistry is continually evolving, striving to identify restorative materials that combine exceptional strength
The eruption of baby teeth is one of the most important stages in a child’s early development.
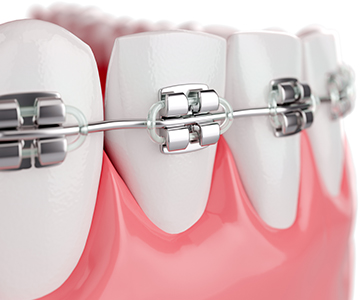
Modern dentistry increasingly emphasizes the importance of orthodontic care.
Oral health care begins long before the first permanent tooth erupts.
A smile is one of the key elements of a person’s visual identity. It conveys confidence and positivity. However, the beauty of a smile is not only an aesthetic factor—it is directly connected to oral health.
Orthodontic treatment has long gone beyond the limits of traditional metal braces.
Dental implantation is the best method for restoring missing teeth. However, for the procedure to be successful, the jawbone must have sufficient volume and density.
Dental implantation is one of the most effective and safest surgical procedures in modern dentistry for restoring missing teeth.
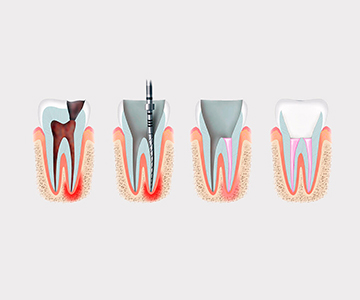
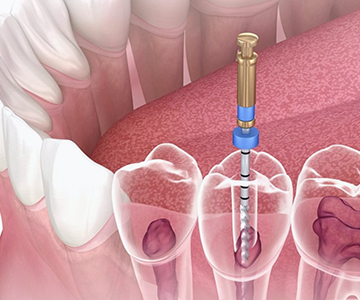
Initial endodontic (root canal) treatment is usually successful and helps preserve the natural tooth.
Root canal treatment, also known as endodontic therapy, is one of the most frequently discussed yet often misunderstood dental procedures.
Tooth decay is one of the most common dental conditions, involving damage to the hard tissues of the teeth
Modern dentistry is constantly evolving, offering improved methods for solving complex issues.
Today, there are numerous teeth whitening options—both at home and professionally done.






.jpeg)
.jpeg)